ABOUT
ENGIE
ENGIE
is a French multinational electricity utility company, headquartered in La Défense,
Courbevoie, which operates in the fields of energy transition, electricity
generation
and distribution, natural gas, nuclear, renewable
energy and Petroleum.
Since
2014, ENGIE has operated a strategic shift, by reducing future exploration
in fossil fuels
and investing massively in renewable energies (solar, wind, geothermal,
biomass, hydroelectric,
and nuclear) and energy efficiency services.
In 2015, ENGIE announced its decision to stop new investments in coal
plants, and to dispose of €15 billion in assets in order to reinvest into
projects that promote low-carbon, distributed-energy. ENGIE also announced
it will invest €22bn in renewable energies, energy services such as
heating and cooling networks, and decentralized energy technology.
In 2016, Isabelle Kocher defines the strategy of ENGIE as follows: to
promote decarbonized energy (oil and coal replaced by renewables and natural
gas that emit less greenhouse
gases), decentralized energy (energy produced and stored as close as
possible to its place of consumption), and digitized energy (big data and
digital tools for energy efficiency and network management). The Group
creates ENGIE Digital and plans to invest €1.5 billion on digital and new
technologies related to energy.
ENGIE is also promoting an open innovation approach with its dedicated
entity "ENGIE Fab" that supports in particular development of
intelligent networks (smart grids), Internet of objects, green mobility,
energy storage, and hydrogen.
STRATEGIC PLAN 2019 - 2021
In
2019, Isabelle Kocher announces the strategic plan of the company for the
2019-2021 period, with an ambition to become the world leader in the
zero-carbon transition. The strategic shift includes accelerating its
investments in renewable energies and focusing on high-value added services
to the clients.
Isabelle
Kocher announces the definitive exit of coal
activities. Engie plans to invest another €12 billion in renewable
activities, partly financed by the sale of €6 billion assets (including
the last coal plants).
The
12 billion break down as follows: 3 to 3.3 billion into gaz infrastructure;
4 to 5 billion into client services and solutions; and 2.3 to 2.8 billion
into renewable energies, adding a 9 GWH production capacity, to reach a
renewable installed capacity of 52 to 64 GW by 2026.
As
far as the services are concerned, Isabelle Kocher's plan is to develop
"energy transition as a service" for large companies and
metropolises, whom she says are driving the "second wave of energy
transition" by searching ways to reduce their carbon
emissions (the first wave having been driven by the states).
She also says it might be "the invention of a new industry" of a 1 billion dollar potential value.
Engie also announces its intention to leave 20 of the 70 countries where it is active, and focus its activities on 20 countries and 30 metropolitan areas, mainly in Southeast Asia and Africa.
It is one of the few players in the sector to develop expert skills in both upstream (engineering, purchasing, operation, maintenance) and downstream (waste management, dismantling) activities.
The company, formed on 22 July 2008 by the merger of Gaz de France and Suez, traces its origins to the Universal Suez Canal Company founded in 1858 to construct the Suez Canal.
As of 2018, ENGIE employs 158,505 people worldwide with revenues of €60.6 billion. ENGIE is listed on the Euronext exchanges in Paris and Brussels and is a constituent of the CAC 40 and BEL20 indices.
ENGIE was headed from 2016 to 2020 by Isabelle Kocher, who has strongly transformed the company since 2016, notably by deciding to exit coal activities and by investing massively in renewable energies and energy transition
services, presumably also to cater for electric
vehicles.
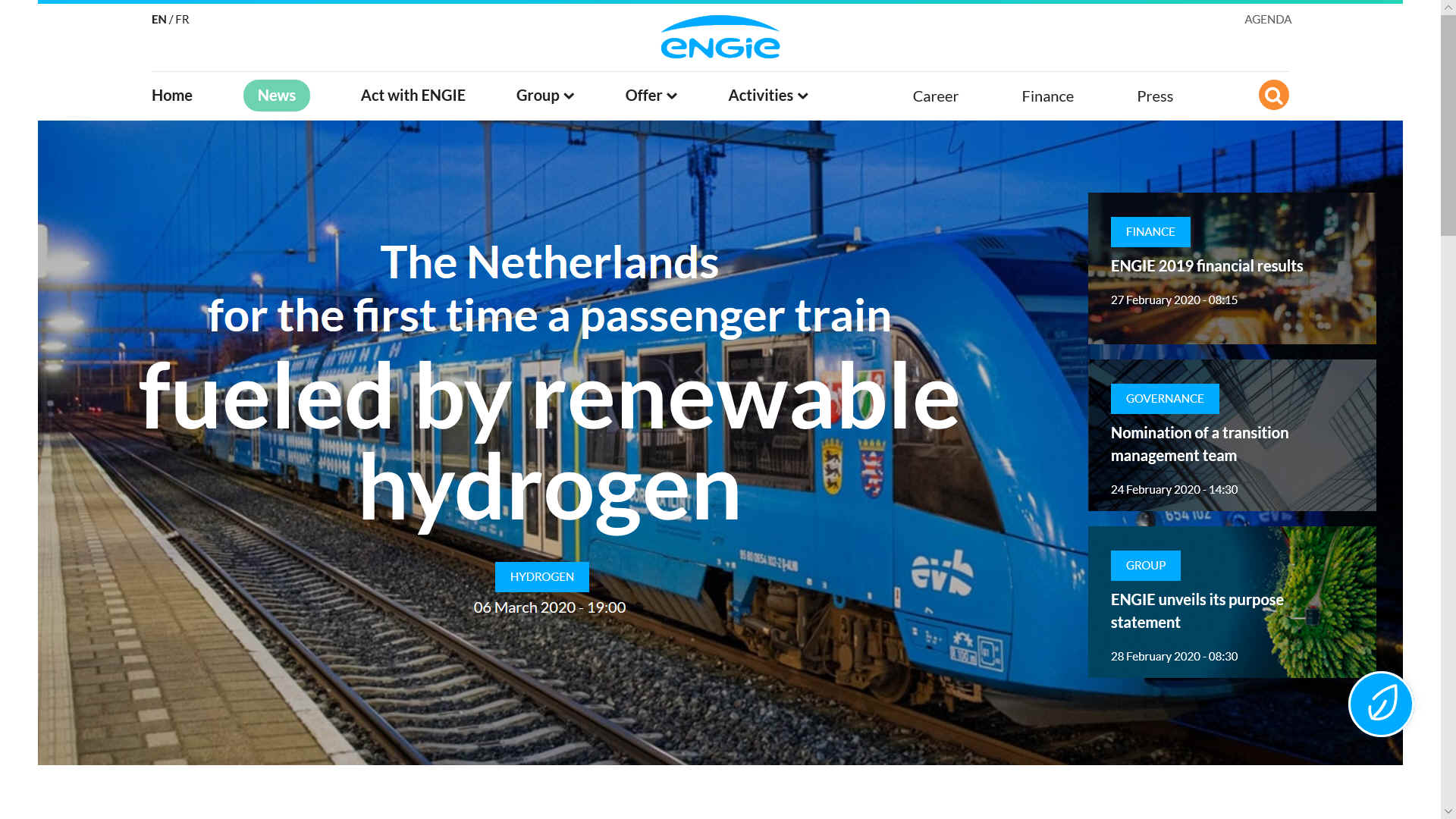
HYDROGEN
VNG BUS & RESIDENTIAL GAS HEATING
ENGIE is trialing the injection of hydrogen into the natural gas
distribution network of a new neighborhood, Le Petit village, and an NGV
refueling station for buses located in the Dunkirk Urban Community. Heating
and domestic hot water needs will be satisfied by an innovative energy
solution: Hythane1, a new gas composed of hydrogen and natural gas. The aim
of the project is to demonstrate the technical, economic, environmental and
social advantages of this new energy solution for sustainable cities and
green mobility in real operating situations.
The French government is supporting the GRHYD hydrogen energy storage
demonstrator project now being conducted by ENGIE and a consortium of
industrial partners2. France has set the target of meeting 23% of its gross
end-user energy consumption from renewable sources by 2020. This ambitious
project aims to convert surplus energy generated from renewable sources into
hydrogen, which will then be blended with natural gas for a broad range of
applications, including space heating, water heating and fuel. As a result,
generators of energy from intermittent renewable sources, such as wind and
solar power, will have a new solution for marketing the electricity they
generate, at the same time as reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
TRANSPORT
Improving the quality of life and developing smarter mobility: public
transport infrastructure, intelligent transportation systems, refueling
infrastructure for green fuels
How to fight against pollution
and global
warming in cities? How to improve traffic flow and safety? The
challenges of green mobility, to which ENGIE provides solutions, are
lowering CO2
emissions, reducing noise and developing accessibility. Cleaner fuels such
as electricity,
gas and hydrogen offer greener, more cost-effective and more convenient
transportation solutions for users. Intelligent transportation systems
optimize existing infrastructure to help communities develop in the light of
their region’s needs and resources. Innovative solutions for harmonious
urbanization.
In December, the EU
Parliament and Member States agreed on ambitious targets for 2030 demanding
a reduction of CO2 emissions from new passenger cars and light commercial
vehicles by 37,5% and 31% respectively. Negotiations on 2030 targets for
trucks are not yet finalized but here as well, ambitious proposals are on
the table.
With the growth of urbanization by 2050, we will have 2.4 billion new
inhabitants and 2/3 of us with live in the city, automobile transport will
almost double and passenger kilometers almost 1.5 times higher. The
consequences are already alarming today, on multiple levels – economic,
human, social and environmental.
On the occasion of Viva Technology 2019, which is being held in Paris
from 16 to 18 May 2019, Ovarith Troeung will discuss the importance of zero
carbon mobility, the cornerstone of sustainable and livable cities.
FRANCE
Thanks to former Suez subsidiaries such as Compagnie Nationale du Rhône (CNR),
Electrabel and Société hydroélectrique du Midi [fr] (SHEM), GDF Suez is
the second-largest generator of electricity in France behind EDF. The
company indicated in December 2011 that ¾ of the group's production comes
from sources that emit no CO2 principally hydroelectricity (through CNR and
SHEM) and wind power, the latter of which both Gaz de France and Suez moved
aggressively into in 2007 and 2008.
Recently
acquired subsidiaries include Compagnie du vent [fr] (majority stake), the
wind farm business of Nass & Wind and Erelia. The company also operates
a natural gas-fired combined cycle power plant (DK6) in Dunkirk. With the
stated aim of reaching a total production capacity of 10 GW by 2013, three
gas-fired thermal power plants at Fos-sur-Mer, Montoir-de-Bretagne and
Saint-Brieuc are currently in various stages of development, as is a solar
panel project in Curbans.
INTERNATIONAL
ENGIE also generates electricity in a number of countries outside France.
Most notably, the company is the leading producer in both Belgium and the
Netherlands through Electrabel (and the fifth-largest generator in Europe
overall), as well as the largest non-state owned generator in both Brazil
and Thailand (thanks to majority stakes in ENGIE Brasil and Glow Energy
respectively).
The company also operates in North and Latin America through its Suez Energy
International unit, as well as in other European and Asian countries. The
company generates electricity through various types of plants, including
thermal power, nuclear power, combined heat and power, wind farms,
hydroelectric and biomass.
ENGIE is currently developing a $15.8 billion nuclear power plant in Sinop,
Turkey in partnership with Itochu and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
In November 2016, ENGIE signed an agreement with Moroccan energy company
Nareva. The two companies are planning to develop energy assets in North and
Western Africa that will produce 5,000 and 6,000 megawatts. The plans will
take place between 2020 and 2025.
In
December 2016, ENGIE announced that Azzour North One Independent Water &
Power Project (IWPP) has started full commercial operations. The power and
water plant is Kuwait's most efficient source of electricity. In January
2017, ENGIE has been awarded the contract and achieved financial closing for
the greenfield Fadhili independent power project (IPP) in Saudi Arabia, the
most efficient cogeneration plant in the country.
COAL FIRED POWER PLANTS
In October 2015, ENGIE announced that it will no longer build coal-fired
power plants. Gérard Mestrallet said projects for which ENGIE had already
entered into firm commitments would be honored, but projects where contracts
had not yet been signed will de facto be suspended. As a result, ENGIE
abandoned two coal-fired power plants projects in Ada Yumurtalik (Turkey)
and in Thabametsi (South Africa).
In February 2016, ENGIE announced the selling of its stakes in the Paiton
power plant located in Indonesia and in the Meenakshi power plant located in
India.
ENGIE also announced the closing of the Rugeley power station in England.
In May 2016 ENGIE CEO Isabelle Kocher told a French
Senate committee that it was planning a gradual withdrawal from coal-fired
generation over the coming years. This could include closure of, or sale of
its stake in, the lignite-fired Hazelwood Power Station in Victoria, Australia.
Hazelwood power plant closed at the end of March 2017.
ENGIE sold to Enea its Polaniec power plant, in Poland.
In February 2019, Engie announced the definitive exit of all coal
activities.

FRENCH
HQ
- Previously known as GDF Suez, Engie SA (ENGI) is a multinational utility company headquartered in France. It has operations in electricity generation and distribution, natural gas and renewable energy. The name change reflects the company’s departure from the state-owned nationalized gas monopoly.
As of 2019, the company has 160,000 employees worldwide and €60.6 billion in
revenues. The firm's market capitalization was € 39.9 billion.
POWER
COMPANIES A - Z Duke
Energy Corporation, DUK, N. Carolina, USA Dominion
Energy Inc., Richmond, Virginia EDF
Électricité de France SA ENEL Engie E.ON Exelon
Corporation EXC, Chicago, USA GE
General Electric Iberdrola KEPCO
Korean Electric Power Corporation National
Electric Grid & Central Electricity Authority (India) National
Energy Board (Canada) National
Grid plc (formerly Central Electricity Generating Board UK) Next
Era Energy Inc. Florida, USA
Scottish & Southern Energy Southern
Company, Atlanta, Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, USA State
Grid Corporation of China TEPCO
Tokyo Electric
Power
Company
CONTACTS Gwladys Huré
- Media Relations
+33 (0)1 44 22 24 35
engiepress@engie.com Engie Groupe
1 PL Samuel Champlain
Courbevoie 92400
France
LINKS
& REFERENCE
https://www.engie.com/activites/renouvelables/solaire
https://www.engie.com/en/activities/infrastructures/transportation
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/integrated-facility-management
https://www.engie.com/en/what-we-do-vocabulary/power-generation
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/gas/hydrogen/power-to-gas/the-grhyd-demonstration-project
https://www.engie.com/en/what-we-do-vocabulary/renewables
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/mobility-today
https://www.engie.com/en/news/windfloat-atlantic-offshore-first-floating-wind-farm-continental-europe
https://www.engie.com/en/candidates/collective-intelligence
https://www.engie.com/en/news/peru-harmonyproject-energy-jungle
https://www.engie.com/activites/renouvelables/solaire
https://www.engie.com/en/activities/infrastructures/transportation
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/integrated-facility-management
https://www.engie.com/en/what-we-do-vocabulary/power-generation
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/gas/hydrogen/power-to-gas/the-grhyd-demonstration-project
https://www.engie.com/en/what-we-do-vocabulary/renewables
https://www.engie.com/en/businesses/mobility-today
https://www.engie.com/en/news/windfloat-atlantic-offshore-first-floating-wind-farm-continental-europe
https://www.engie.com/en/candidates/collective-intelligence
https://www.engie.com/en/news/peru-harmonyproject-energy-jungle
Please
use our A-Z
INDEX to navigate this site
|

